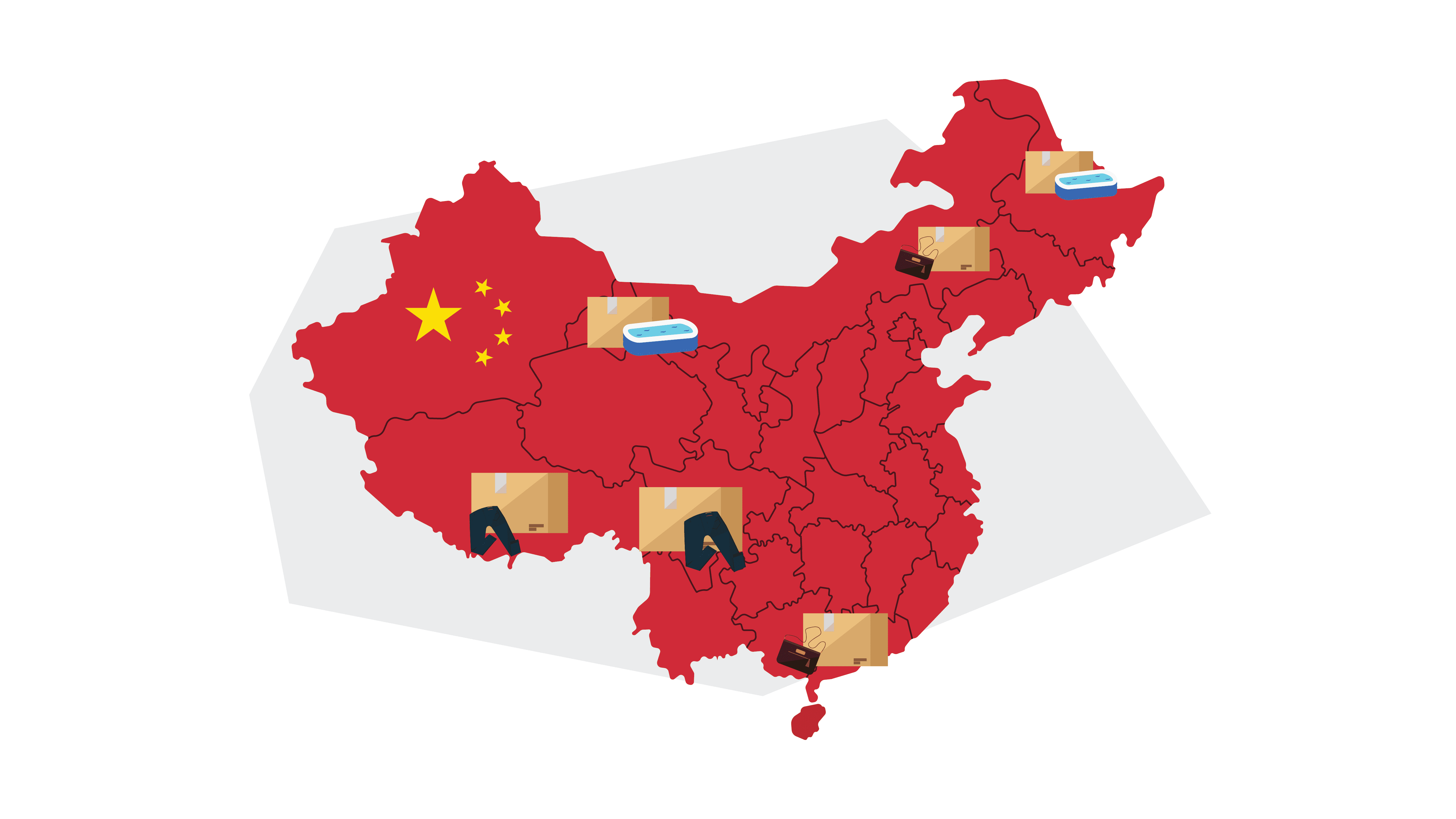
Popular Manufacturing Hubs in China

This is a guest post from Leeline Sourcing. Leeline Sourcing is a sourcing partner that can help eCommerce merchants tap into valuable Chinese markets and suppliers with faster, more effective results.
After joining the World Trade Organization (WTO), China became the world’s largest manufacturer. It’s not wrong to call China the “world’s factory.”
China remains one of the best locations for manufacturing eCommerce goods thanks to favorable local policies, abundant labor resources, and a number of other factors that favor the manufacturing industries.
The value-added industrial output in China has continuously increased. In fact, 28.7% of the world’s manufacturing output has taken place in China. Many international companies tap the Chinese workforce to produce their products, including Apple, Volkswagen, Bright Food, Tesla, Baosteel Group, Fosun Group, Yotex Apparel, and General Motors.
In this article, we’ll discuss popular manufacturing hubs in China and which area they specialize in.
Top 8 manufacturing hubs in China
The eight main manufacturing hubs across China are:
- Shanghai
- Shenzhen
- Hongkong
- Ningbo
- Qingdao
- Guangzhou
- Hangzhou
- Tianjin
1. Shanghai
Shanghai is China’s most critical economic center-point area. It has become the busiest port in the world, with more than 2,000 container ships leave the port each month, delivering cars, electronics, and clothes to the world.
This hub plays a crucial role in China’s industry, especially in the automotive market. Shanghai is home to the country’s biggest companies, Volkswagen and General Motors, all located their plants here.
Shanghai is also the headquarters for multinational corporations’ China operations: Apple, L’Oreal, Samsung Electronics, P&G, L’Oreal, LVMH, Nike, Panasonic, Philips, Johnson & Johnson, and General Electric. In Shanghai, you can see a famous brand factory of any major in every blink.
2. Shenzhen
Since the 1980s, Shenzhen has developed into one of China’s main hubs of the electronics market. It ranks as the second busiest port, right after Shanghai.
The world’s most popular brands, LG, Huawei, and ZTE, utilize their manufacturing in Shenzhen. At the same time, giants like Walmart have a headquarters and global procurement center here.
Here you can also find telecommunications and computer plants. And if you have ever heard of Shenzhen, you might know the term “China’s Silicon Valley” for this area.
3. Hong Kong
Besides its popularity for tourism, Hong Kong is a significant manufacturing and financial hub in the country.
There’s no doubt Hong Kong, the city that never sleeps, still retains its “throne” in China’s economic growth till these days.
Hong Kong is well known for textile and clothing production and electronics such as medical equipment and other innovative technology.
4. Ningbo
South of Shanghai, Ningbo has enjoyed rapid growth thanks to its location. Its unique location allows you to move easily between busy ports. It’s now remembered as one of China’s national logistic hubs. As a result, Ningbo Port is one of the busiest ports in the world and certainly the most crowded.
The Ningbo region furthermore specializes in producing a variety of chemicals, electrical machinery, telecom equipment production, and IT devices.
This city also has many manufacturers producing stationary and domestic electronic items.
5. Qingdao
Qingdao lies around the eastern Shandong Province, near the Yellow sea coast, making it one of China’s most important harbor cities. The manufacturers in Qingdao mainly focus on producing electronic appliances, garments and textile machinery.
Qingdao is also one of China’s major economic engines with diverse manufacturing in biopharmaceuticals, fine chemicals, petrochemicals, automobiles, building materials, and metallurgy.
6. Guangzhou
Guangzhou in Southern China, or the ‘Canton City,’ hosts the most significant international trade fair each year. Although there’s no direct sea entrance, Guangzhou has still become a central national economic hub thanks to its crucial location. This capital city owns one of China’s large ports and offers a direct route to Taiwan, conveniently accessible to various significant highways or railways.
Guangzhou is a place to consider if your business involves auto parts, mobile accessories, toys, petrochemical, electronics, or apparel. Leading automotive brands like Honda, Nissan, Sony, Panasonic, and Toyota have manufacturing plants in Guangzhou.
7. Hangzhou
Moving to the East, Hangzhou is emerging as a competitive manufacturing hub in the country. It hosts many exhibitions, including the World Leisure Expo every year.
Hangzhou is home to Alibaba, the biggest eCommerce giant in China. Many textile industries are well-established here.
8. Tianjin
Tianjin, a city in Northern China, is one of the booming industrial cities where the mechanical and textile industries are flourishing. It is also leading in aerospace & aviation and alternative energy products.
Benefits of manufacturing in China
1. Lower cost of living = lower wages
The wages in China remain low compared to Western standards thanks to a lower cost of living, along with a greater supply of workers than demand.
Major industrial cities have a giant workforce that encompasses many roles and talents. As a result, the vast labor pool in China helps to produce in bulk and can adapt to sudden rises in the schedule.
2. A growing business ecosystem
In the last 30 years, the business ecosystem in China has grown enormously. To see the evidence of this, take a look at Shenzhen, which has developed as a hub for the electronics industry.
The region has nurtured an ecosystem to support the manufacturing supply chain, including component manufacturers, low-cost workers, a technical workforce, assembly suppliers, and customers.
For example, Foxconn Technology Group takes advantage of that by having multiple suppliers and manufacturers of components at nearby locations. This Taiwan-based manufacturer of electronics successfully keeps costs low and margins high.
3. Access to materials
The geographically large country of China is rich in not just talent, but also resources. Thanks to a wealth of land, it becomes easier to acquire raw materials that may require more space – for example, growing the plants needed to create textiles. This provides an advantage in sourcing and helps to ensure supply.
4. Taxes and duties
In 1985, the China government enacted the export tax reduction policy, totally banning the double taxation on exported goods. Exported goods enjoyed a VAT exemption or a good rebate. This low export rate is a great way to make China stand out among competitors.
Another deal, consumer products don’t need to account for the import taxes. This policy was born to attract investors and companies looking to produce low-cost goods. And it also helps to keep the cost of production low.
4. Currency
China artificially pushed the value of its yuan to provide an edge for its exports against competitors.
In 2019, China’s central bank lowered the yuan to 7.0205 per dollar, the weakest level since 2008. The weaker yuan makes Chinese exports look more attractive.
Common FAQs about manufacturing in China
Below we’ll discuss some of the most common questions we get about manufacturing in China.
How is China coping financially after the pandemic?
The COVID-19 pandemic hit triggered another massive global supply chain shake-up, beginning with China’s shutdown. The pandemic also created shock waves across many multinational companies. They discovered how much they depended on Chinese manufacturing, from raw materials to production facilities and supply chain. They spend all their effort prompting many to start looking for alternative locations.
Stay or go is the biggest question. And it isn’t easy to answer. Business leaders will need to evaluate the supply chain and the company’s financial standing and ability to invest. Ensure that a robust supply chain strategy is in place given the significant investment and against the risk involved. The timing on whether to be the first mover or to adopt a wait-and-see approach will also play a crucial role in business leaders’ decisions.
Will China still be the place to be a decade from now? And if not, what’s next?
With the amount of resources and infrastructure set up, equipping China to be the manufacturing hub of the world, it makes logical sense that the country will continue to maintain a strong position within global markets.
However, be sure to research your specific product and manufacturing needs to determine the best course for your unique business.
What does China mainly produce?
China is always ahead in the manufacturing of various products. Mining and ore mining is one of the major industries of China. Iron, steel, aluminum, concrete, toys, hardware, rail vehicles, and boats are also China manufacturing’s strengths.
Which industries are booming in China?
The top three sectors driving growth for China include the services industry, manufacturing, and technology.
Software and internet services are the “young but gold” today. Statistics show there were 147,781 software development businesses in China as of January 2022. As COVID-19 continues, software and internet demands are getting bigger and bigger.
What is the most industrial region in China?
Hong Kong, Shanghai, and Beijing place in the first three ranks of the most industrial hubs in the ranking.
Conclusion
Among the global trade wars, China has a strengthening position as the world’s leading manufacturing hub. Thanks to low production costs, access to materials, large labor and talent pools, and a growing business ecosystem, China will remain a go-to for manufacturing across the world.
Have you acknowledged the potential manufacturers in China but don’t know where to start yet? Leeline Sourcing can help you keep your time and money spent to a minimum. Thanks to years of experience, our professionals know which is best for manufacturing your product in China.


